SyncCenter™
The SyncCenter is Fibrolan's unique technology designed to simplify system’s timing behavior control and monitoring, while maintaining a high degree of flexibility.
SyncCenter offers the following key advantages:
- Simple selection of Timing sources, designed to simultaneously combine multiple interface types (GNSS, PTP, SyncE, ToD, NTP, etc.)
- Align all the system's Timing outputs with the selected source
- Flexible setting of the system Holdover behavior
- Real-time monitoring of the sources
- Manul setting of system Time of Day (ToD)
- Hitless recovery from a Sync Loss event
- Enabling GNSS-free GM operation (freerun)
Learn more about Fibrolan’s products supporting this technology in the links below:
Flexible Source Selection
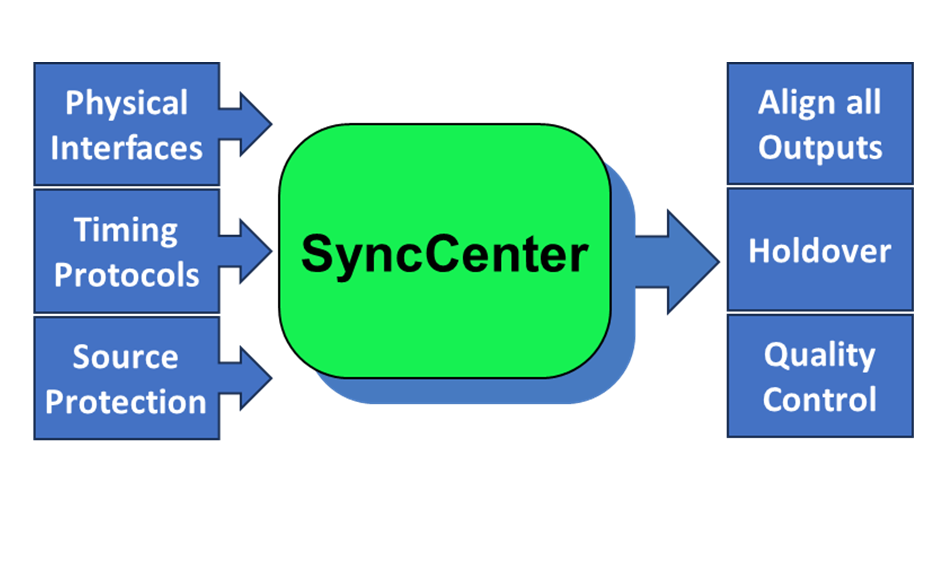
As the name implies, the SyncCenter is the Falcon’s core function governing over all Timing operations and clocking architecture. It is assigned to collect any of the system’s multiple Timing interfaces and protocols, then lock on the designated source(s). Once the SyncCenter reaches Locked state, all the timing interfaces and protocols can be used to propagate the Frequency/Phase/ToD using the same quality level of the source signal. All outputs are aligned to the system’s clock (some outputs allow additional configurable offsets).
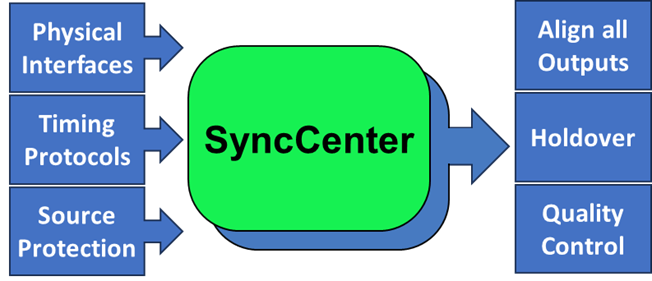
The supported input/output interfaces include:
- Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) – input only
- Ethernet: 100M, 1GE, 2.5GE, 10GE and 25GE
- Clock signals (coax/SMA): 10MHz and 1PPS
- Time of Day (ToD) serial port
- Building Integrated Timing Supply (BITS)
The supported input/output protocols include:
- Precision Time Protocol (PTP)
- Synchronous Ethernet (SyncE)
- Network Timing Protocol (NTP)
Multi-Layered Redundancy
The SyncCenter supports up to 5 concurrent active inputs, which provides a highly flexible redundancy scheme. This capability allows the Falcon to be locked on a specific Timing source, while 4 additional sources are configured as backup (with a virtual lock, for fast switchover) in case the primary source fails.
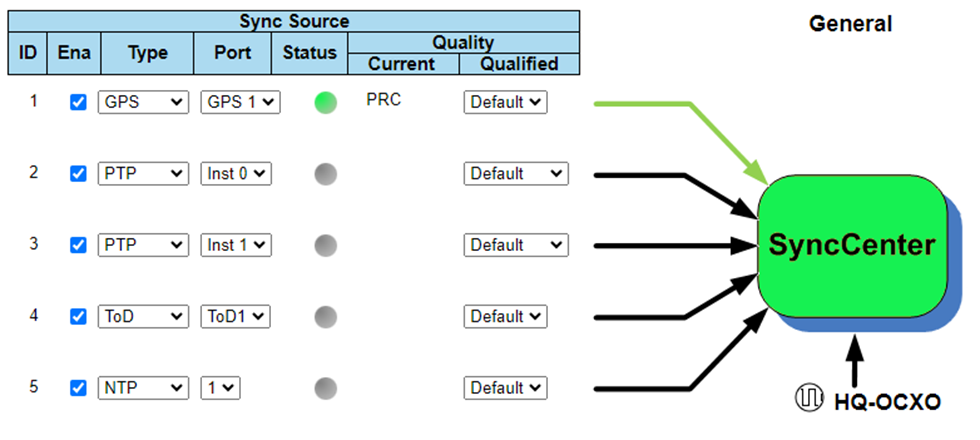
Holdover and Service Disruption
The SyncCenter includes three Holdover timers designed to mitigate short term or intermittent disruptions of the configured timing sources. The goal of this mechanism is to prevent network instability, during source outages (e.g. GNSS). Under such conditions, clock quality distribution may cause client equipment to disqualify the source (e.g. PTP GM). In mobile networks, this can lead to interferences and even service outages. The timers, being fully configurable, allow the user to control these kind of unstable conditions, resulting in a stable mobile service.

Offset Monitoring & Mitigation
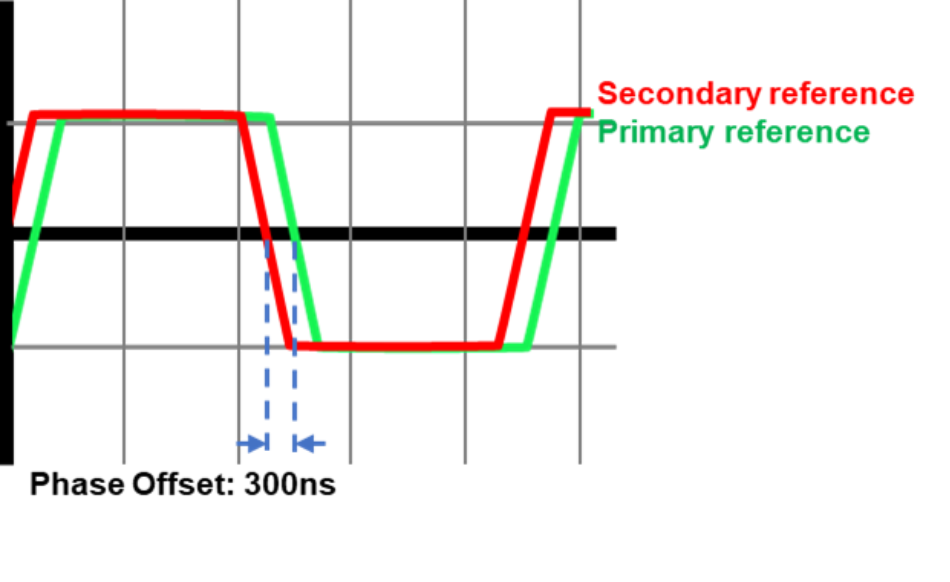
Different clock sources are usually not perfectly aligned, which results in a certain measure of offset in phase between them. The reasons for this offset are most often network topology and network inherent impairments (asymmetry).
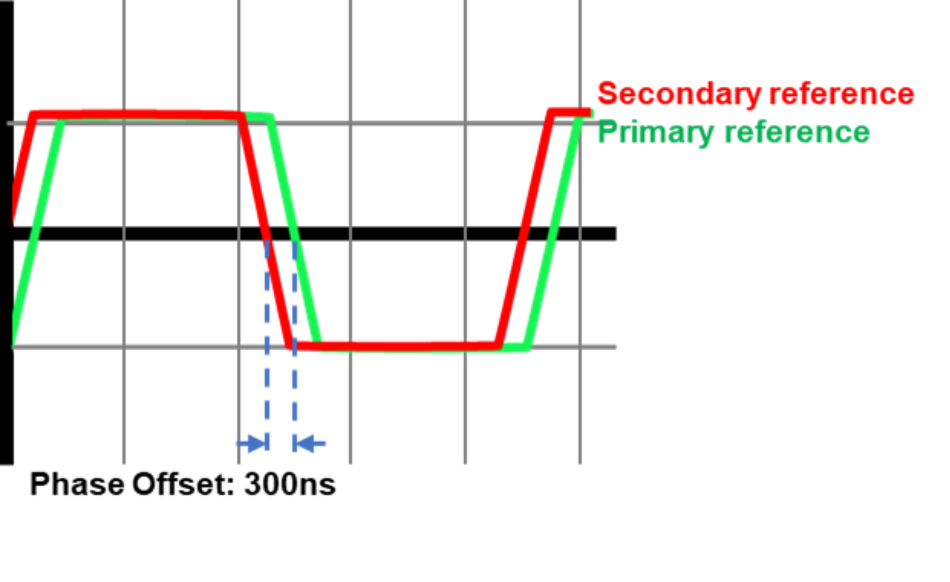
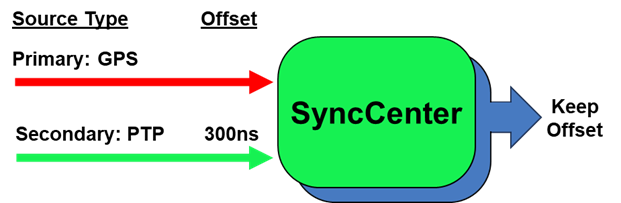
In a topology where one or more alternative sources are part of the design, any major and rapid shift in the signal phase, due to a source swap in case of a failure of the primary source, will have an impact on the slave devices. In addition, network conditions may result in an offset between e.g. GNSS and PTP.
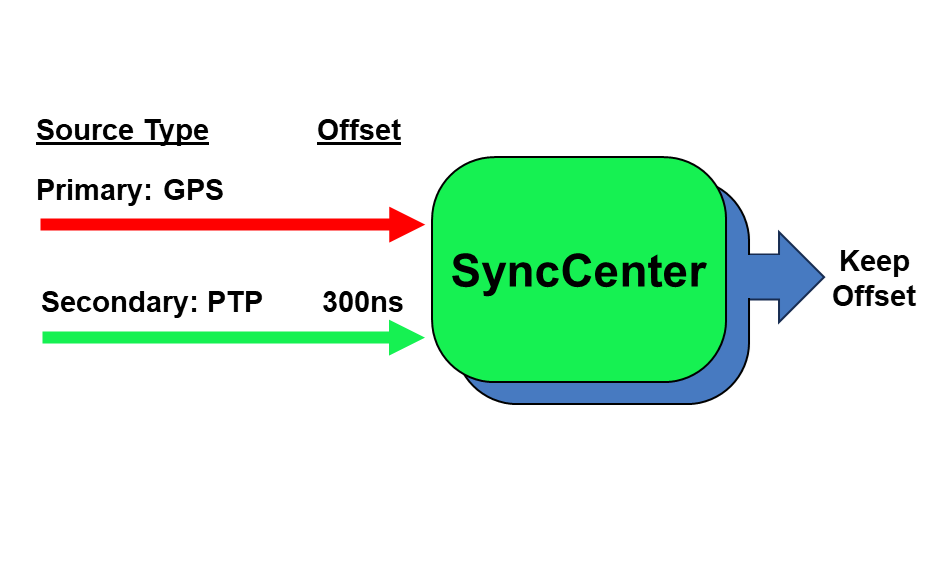
To better measure and monitor the offsets between the different sources and to mitigate the effect of a shift in the signal phase, the SyncCenter measures the existing offset of the additional four alternative sources from the active primary source. Knowing these offset values not only helps the user to compensate for inherent asymmetry of the transport network, but also allows the SyncCenter to smoothly shift to an alternative source when the primary is lost (including the option to maintain the offset, as in APTS).
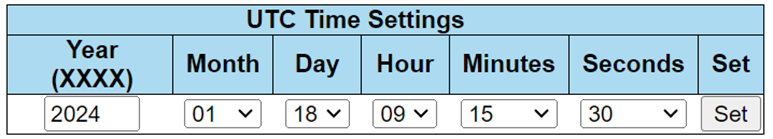
ToD Manual Setting
This useful function allows the user to manually set the current ToD even when no active source such as GPS or PTP is available. It is usually required in lab settings, isolated environments (e.g. subterrain facilities) or short demonstration showcases, when GPS is not available or requires significant efforts to obtain.